Showing posts with label automotive. Show all posts
Showing posts with label automotive. Show all posts
Amazing Video from Toyota Teams:
the video show internal engine parts, engine testing, engine disassembling methods, and a various information abut Engine overhaul
Follow us on Facebook Page
5- BAS (Brake Assist System)
What is BAS?It then provides very high braking power, even when the driver is only pressing gently on the brake pedal.
When this is used together with anti-lock braking systems, it success in faster and safer braking.
 |
| BAS Action chart |
Some road tests show that a driver requires up to 240 feet (73 meters) to stop a car heading around 60 mph (100 km/h).
In the same circumstances, cars with brake assist were able to come to a complete stop in as little as 130 feet (40 meters).
Since it only takes one-fifth of a second to travel a car length at highway speeds, the superior speed with which the brake assist is able to react also accounts for its improved safety results over traditional braking systems.
Press to Watch Brake System Video 1
Press to Watch Brake System Video 2
Press to Watch Brake System Video 3
Read About ABS : Press Here
Read About ESP : Press Here
Read About ESC : Press Here
Read About EBD: Press Here
Read About LSD: Press Here
Read About BAS: Press Here
follow us on Facebook: FaceBook
4- LSD (Limited Slip Differential)
A limited slip differential (LSD) is a modified or
extracted type of differential gear arrangement that allows for some
variation in rotational velocity of the output shafts, but does not
allow the difference in speed to increase beyond a preset amount. In an automobile, such limited slip differentials are sometimes used in place
of a standard differential, where they convey certain dynamic
advantages, at the expense of greater complexity.  |
| LSD Effect On The Road |
The main advantage of a limited slip differential is found by considering the case of a standard (or "open") differential where one wheel has no contact with the ground at all.
In such a case, the contacting wheel will remain stationary, and the non-contacting wheel will rotate freely
the torque transmitted will be equal at both wheels, but will not exceed the threshold of torque needed to move the vehicle, thus the vehicle will remain stationary. In everyday use on typical roads, such a situation is very unlikely, and so a normal differential suffices.
For more demanding use, such as driving in mud, off-road, or for high performance vehicles, such a state of affairs is undesirable, and the LSD can be employed to deal with it. By limiting the velocity difference between a pair of driven wheels, useful torque can be transmitted as long as there is some friction available on at least one of the wheels.
Press to Watch Brake System Video 1
Press to Watch Brake System Video 2
Press to Watch Brake System Video 3
Read About ABS : Press Here
Read About ESP : Press Here
Read About ESC : Press Here
Read About EBD: Press Here
Read About LSD: Press Here
Read About BAS: Press Here
follow us on Facebook: FaceBook
3- EBD (Electronic brake force distribution)
What is EBD?
When a rotating wheel is subjected to excessive heavy braking, it is prone to lock-up. In motor vehicles,
the anti-lock braking system (ABS) works to prevent this by monitoring wheel speeds and taking action in the form of releasing pressure on the braking circuit, when a rapid deceleration occurs in any of the wheels to ensure steering and vehicular control is maintained during heavy or emergency braking. This has its disadvantages though, as different amounts of braking pressure are required to lock a rotating wheel on different surfaces.
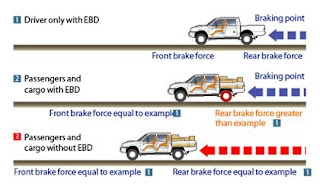 |
| EBD Operation |
here is an example to explain how EBD work, less braking pressure would be needed to lock a wheel which was in contact with ice than a wheel which was in contact with an asphalt road.
In a situation where the wheels of a vehicle are on different surfaces (for example the two left wheels are on a concrete road and the two right wheels were on snow), during an emergency stop ABS would detect the two right wheels about to lock and would activate, even though the two left wheels would not have locked when the right wheels did.
EBD detects such conditions and electronically controls the braking force applied to each individual wheel, and therefore maximizes the braking force to ensure a maximum braking effectiveness. The final result is more precise and effective braking under all conditions, and also makes the car much more stable under heavy braking, reducing front end dive
Press to Watch Brake System Video 1
Press to Watch Brake System Video 2
Press to Watch Brake System Video 3
Read About ABS : Press Here
Read About ESP : Press Here
Read About ESC : Press Here
Read About EBD: Press Here
Read About LSD: Press Here
Read About BAS: Press Here
follow us on Facebook: FaceBook



